Wrapping Command-Line Tools
Let’s say you want to improve cd:
- after cd, print the current directory

- given a filename, cd to the directory containing the file
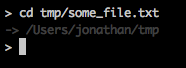
Here’s something that won’t work:
cd() {
# check if path is a file, etc
cd "$dest"
# print pwd
}The problem is that cd calls itself recursively. Maybe there’s a way around
this with clever aliases. Maybe you could call your version mycd… but you’ve
been typing cd for years, and you’re working against your muscle memory.
Thankfully, there’s a workaround for this specific problem:
cd() {
# check if path is a file, etc
builtin cd "$dest"
# print pwd
}(my full cd code is available in my dotfiles.)
The key part is the builtin cd invocation which prevents a recursive loop.
builint cd calls the real cd from the shell. The same trick works for
commands that aren’t builtin, for example, command ls would bypass aliases and
functions named ls and look for something in the PATH.
From the bash man page:
builtin shell-builtin [arguments]
Execute the specified shell builtin, passing it arguments, and
return its exit status. This is useful when defining a function
whose name is the same as a shell builtin, retaining the func-
tionality of the builtin within the function. The cd builtin is
commonly redefined this way. The return status is false if
shell-builtin is not a shell builtin command.
command [-pVv] command [arg ...]
Run command with args suppressing the normal shell function
lookup. Only builtin commands or commands found in the PATH are
executed. If the -p option is given, the search for command is
performed using a default value for PATH that is guaranteed to
find all of the standard utilities. If either the -V or -v
option is supplied, a description of command is printed. The -v
option causes a single word indicating the command or file name
used to invoke command to be displayed; the -V option produces a
more verbose description. If the -V or -v option is supplied,
the exit status is 0 if command was found, and 1 if not. If
neither option is supplied and an error occurred or command can-
not be found, the exit status is 127. Otherwise, the exit sta-
tus of the command builtin is the exit status of command.
I was playing with docker recently, and the documentation said to call
boot2docker shellinit to set some environment variables before calling the
docker command. Life is too short for that …
- I don’t want to remember to call a command
- I don’t want to remember what command to call
- I don’t want to type that command either
docker() {
if [ -z "$DOCKER_HOST" ]; then
eval "$(boot2docker shellinit)"
fi
command docker "$@"
}If DOCKER_HOST isn’t set, call boot2docker shellinit, then call docker
like I asked.