Sending HTML to Mailgun with cURL
I used to run Postfix and have it send my emails through Mailgun, mostly for the reasons explained in The Hostile Email Landscape.
But Mailgun accepts emails from a POST request, so I thought it would be a good opportunity to get rid of Postfix on my virtual private server.
Mailgun and cURL
On their main page, Mailgun shows you how to send an email with curl:
curl -s --user "api:$API-KEY" \
https://api.mailgun.net/v3/samples.mailgun.org/messages \
-F from='me@example.com' \
-F to='you@example.com' \
-F subject='Hello' \
-F text='how are you?'That works fine, but it’s overly simplified. Here’s what I need to know:
- how to send HTML
- how to send multiple lines
- how to pipe to curl (have curl read from STDIN)
Some answers:
- use
html=...to send HTML, they have examples in the Mailgun documentation. - in curl, you can replace a value with
@filenameto read from file @-reads from STDIN
Based on their documentation and putting it all together, I tried this:
cat some.html | curl -s --user "api:$API-KEY" \
https://api.mailgun.net/v3/samples.mailgun.org/messages \
-F from='me@example.com' \
-F to='you@example.com' \
-F subject='Hello' \
-F html="@-"but kept getting this error:
{
"message": "'html' parameter is not a string"
}
It could have been easy: Mailgun could cover more (realistic) cases in their documentation. As it stands, even when they send HTML, it just a one-liner.
The Solution
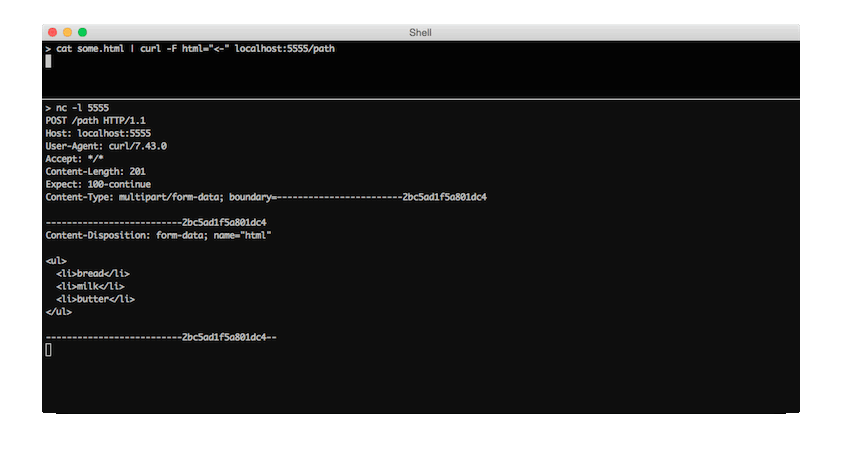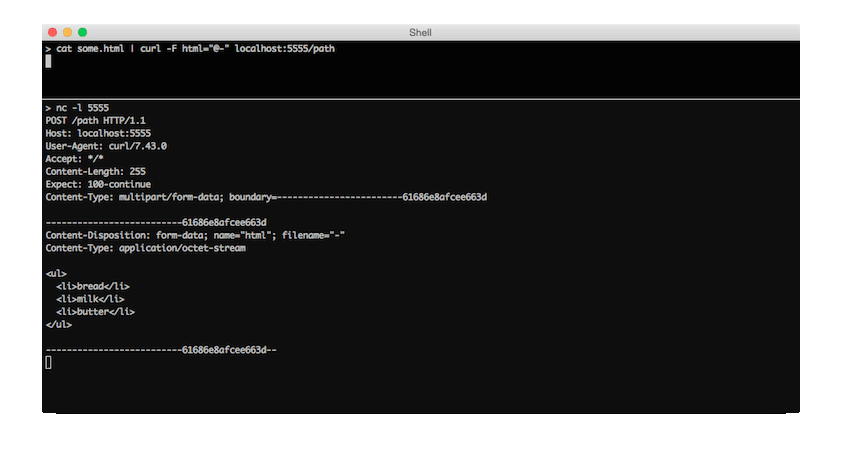
I had never seen an example of this, but you can change @- to <-:
cat some.html | curl -s --user "api:$API-KEY" \
https://api.mailgun.net/v3/samples.mailgun.org/messages \
-F from='me@example.com' \
-F to='you@example.com' \
-F subject='Hello' \
-F html="<-"The < means send the file ‘as text’, not as a file. The curl man page itself:
-F, --form <name=content>
(HTTP) This lets curl emulate a filled-in form in which a user
has pressed the submit button. This causes curl to POST data
using the Content-Type multipart/form-data according to RFC
2388. This enables uploading of binary files etc. To force the
'content' part to be a file, prefix the file name with an @
sign. To just get the content part from a file, prefix the file
name with the symbol <. The difference between @ and < is then
that @ makes a file get attached in the post as a file upload,
while the < makes a text field and just get the contents for
that text field from a file.
You can see the difference in a netcat capture of both commands:
Finally, I packaged this curl command in a script to replace both the postfix and the mailx-bsd packages.
> cat /usr/local/bin/send-with-mailgun # replace variables with your values
#!/bin/bash
curl --user "api:$API-KEY" \
https://api.mailgun.net/v3/${MAILBOX}/messages \
-F html="<-" "$@"
> cat some.html | send-with-mailgun -F subject="Hello" -F to="you@example.com" -F from="me@example.com"